Explore what VR training is, its benefits, and its use in industry
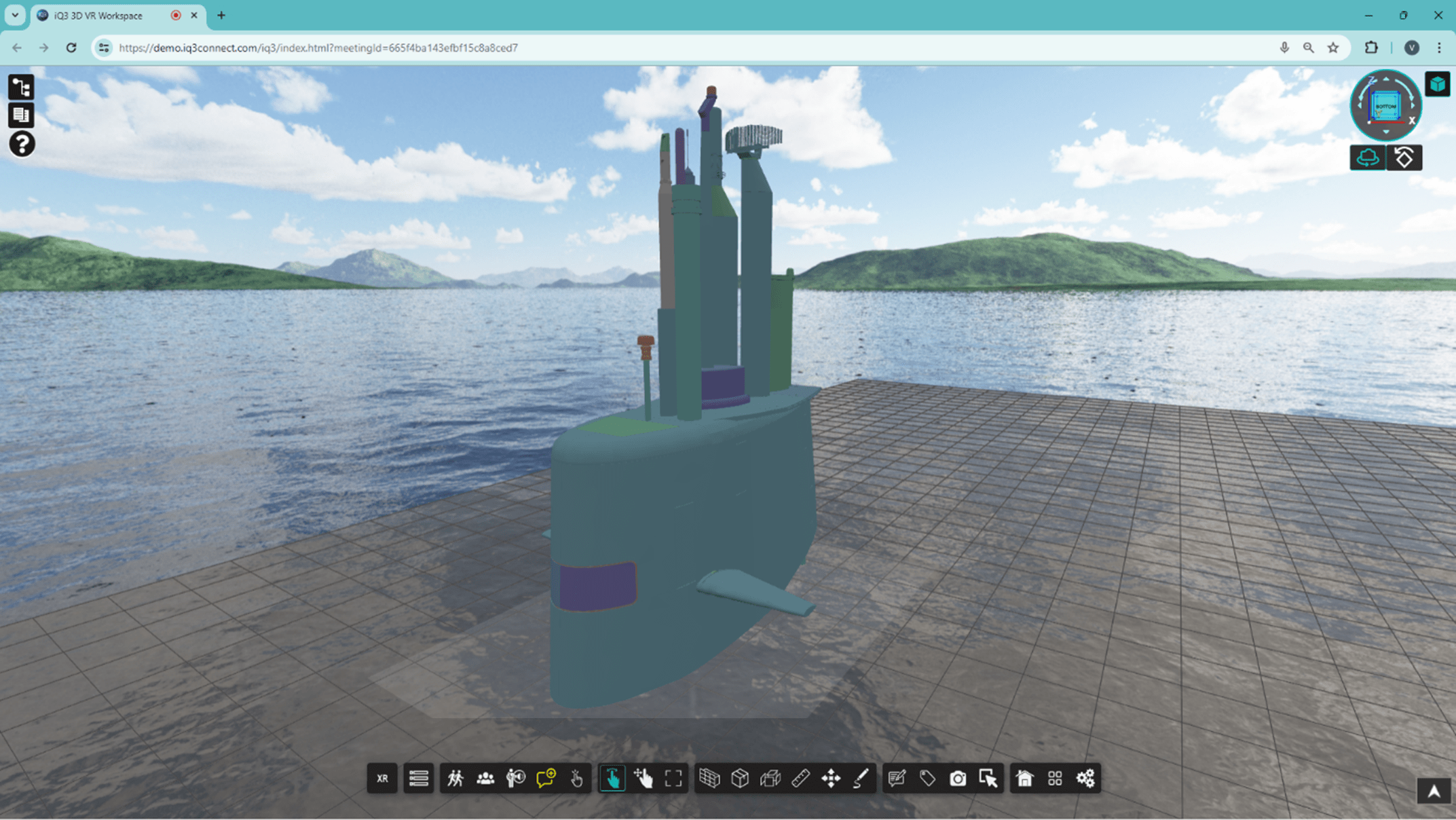
Virtual Reality (VR) training, at its most fundamental, is an immersive e-learning experience occurring within a three-dimensional (3D) virtual environment. It is commonly described as a way to digitally simulate lifelike scenarios for training purposes, enabling trainees/instructors to visualize and interact with the virtual environment (whether tools, machinery, or other trainees/instructors) in a physically realistic manner.
What’s often overlooked, however, is the additional value provided by VR training in its ability to supplement and enhance training scenarios in inherently artificial ways that ultimately serve to improve context and comprehension.
In the manufacturing industry, for example, VR training is used to train new employees on proper safety procedures and to train new technicians on assembly processes by digitally simulating the real-world environment. This lifelike simulation is further enhanced by strictly virtual components such as spatial text, contextual real-time hints, and other means of feedback and interaction that serve to improve comprehension and knowledge retention.
VR training can be used to visualize and interact with objects in ways that are impossible in the real-world – whether visualizing the inner components of an engine in operation or interacting with molecules scaled up to the size of basketballs. This combination of realism and artificialism offers unique opportunities for anyone to learn about complex topics in an intuitive way.
It is this unique opportunity that explains why VR training is used extensively in industries as diverse as construction, healthcare, and manufacturing and for use cases as varied as surgery, virtual assembly and maintenance, health and safety, and general knowledge.
Benefits of VR Training
VR training can offer substantial benefits over both in-person/hands-on training and traditional e-learning (slide decks, videos, online course, etc.).
Unlike in-person classroom training, VR training provides trainees the ability to learn from anywhere at any time and provides opportunities for training that would be too dangerous, difficult, or expensive in a classroom environment. And while traditional e-learning can provide some of these same opportunities, it lacks the realism and immersiveness provided by VR.
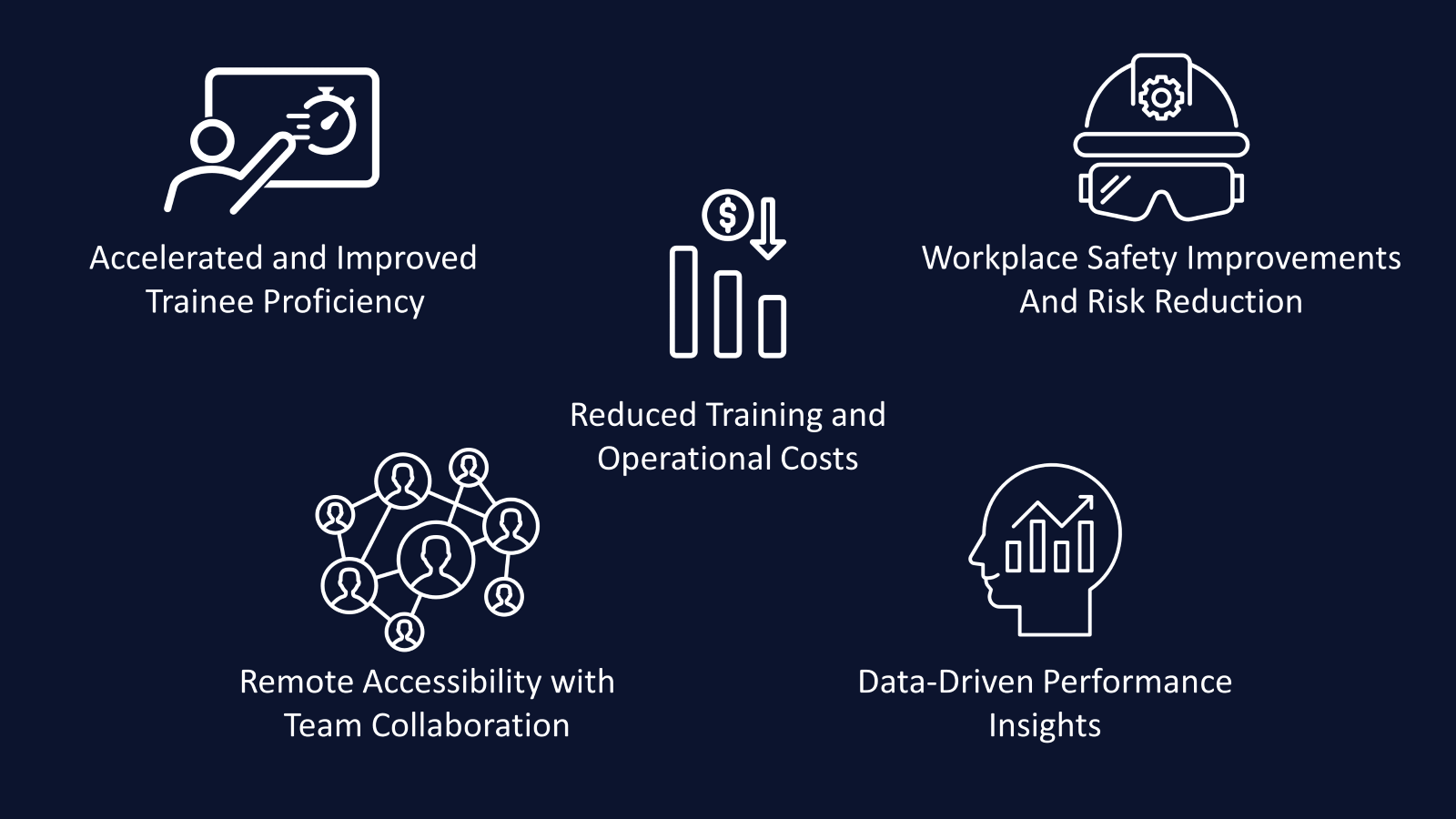
Trainee performance (both in the training and once on the job) and cost (time and money) are often the benchmarks used when evaluating the success of a new training program. In these categories, VR training is well documented to produce substantial benefits.
In a study conducted by PwC, VR learners were 4x faster to train compared to classroom training and 1.5x faster to train compared to e-learning, while being nearly 40% more confident to apply the skills they had learned.
Various studies on VR training for emergency evacuations showed that VR training could provide a 50% reduction in training costs over a 3-year period, while VR trainees performed significantly better compared to traditional learning methods. Intel estimates that their first VR training has a 5-year ROI of 300% and will reduce electrical safety incidents by 28%.
It may be helpful to understand how and why VR training can produce such benefits over more traditional learning methods.
At a fundamental level, VR training is a more engaging experience both physically and mentally, leading to a more active learner and more knowledge retention. iQ3Connect surveys of trainees found that 95% of them preferred VR training over slide deck and video learning with 76% of them identifying immersive interaction with the 3D virtual environment as a critical part of their training experience.
Understanding Virtual Reality (VR)
The term VR training is used in this article as Virtual Reality (VR) is one of the most commonly known terms, the other being Augmented Reality (AR), the defines a subset of immersive technologies along the reality-virtuality continuum – a term that encompasses all technologies operating along a spectrum from the real-world at one end to the completely virtual world at the other end.
Extended Reality (XR) is generally used as the catch-all term for the set of technologies within this reality-virtuality continuum and is most commonly broken down into 3 categories:
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Mixed Reality (MR)
As technology has progressed, the distinction between these categories has blurred to the point that they may be approaching obsolescence. For the moment, however, distinct definitions may be helpful to understand the differing levels of immersion (i.e. completely virtual to blended virtual/real). Know that there is much overlap and clear distinctions are becoming rarer.
Virtual Reality (VR): is a 3D, completely virtual environment that immerses the user in the virtual world. The user has no visual of the real world.
Augmented Reality (AR): is a blend of the real world and virtual, achieved by overlaying virtual objects onto the real world. The user can see both the real world and the virtual simultaneously. This is most commonly experienced in mobile AR apps (think of placing virtual furniture into an actual room), but AR glasses/headsets are also prevalent.
Mixed Reality (MR): is defined differently depending on the source. All sources agree that mixed reality is a blend of the real world and virtual. Some use the terms AR and MR interchangeably while others argue that there are important distinctions between AR and MR involving how the virtual and physical worlds interact with one another. A select few argue that MR is the entirety of the reality-virtuality spectrum encompassing both VR and AR, and thus use MR as the catch-all term for immersive technology.
To summarize, VR is reserved for completely virtual experiences, AR and MR are generally used for blended virtual and real-world experiences, while XR is used to refer to them all.
But as the technology continually evolves, terminology will change and the capabilities offered within each category will continue to bend and alter the definitions.
Many devices, and some software, on the market are no longer exclusive to VR or AR as they can support various levels of immersion. For example, devices advertised as VR headsets are offering MR experiences by enabling external cameras to pass live video feeds of the real world to the user’s display, enabling a merging of the virtual and physical.
When considering VR training, it will be of greater importance to pay attention to specific capabilities of the hardware and software to ensure alignment with one’s objectives, as opposed to relying on VR, AR, MR, or XR labels. In fact, this article, due to public perception and popular understanding of immersive technology, has been using the term VR training exclusively, even though AR, MR, and XR are equally applicable in this context.
Implementation of VR Training in Industry
It is well documented that companies such as Applied Materials, Boeing, Bosch, Ford, LG, Schlumberger, etc. have successfully implemented VR training programs.
These companies, despite coming from a diverse set of industries, including aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, semiconductor, and oil and gas, all faced similar challenges when trying to train and upskill a large global workforce: increasing costs, a drive toward sustainability, and a goal for improved training outcomes. Yet, they have approached VR training implementation in different ways to meet their unique circumstances.
For a large manufacturing company, the time and costs associated with travel (most of it international) for onsite technician training was becoming unsustainable. Additionally, providing the training department with equipment on which to train, even when drastically simplified from production models, was costing well over $1,000,000.
To reduce travel and physical equipment costs, they deployed VR training in the form of multi-user virtual classrooms, enabling an instructor to simultaneously teach 10-15 technicians, remotely, on a digital twin of the physical equipment.
For a company in the consumer electronics market, their implementation of an e-learning curriculum wasn’t achieving the desired results in terms of trainee performance once on the job.
They extended their traditional e-learning offering by incorporating self-paced VR training directly into their LMS platform. These VR training experiences offer self-guided training, accessible on either a VR headset or PC/mobile device, that provide a more realistic and experiential learning environment, leading to improved knowledge retention and on-the-job performance.
Regardless of the exact approach, VR training has been used in industry for training use cases such as plant safety, product knowledge, product assembly, appliance repair and maintenance, onboarding of sales & marketing personnel, facility operations, etc.
Overcoming Barriers to VR Training Adoption
There are typically three barriers that inhibit companies from adopting VR training at scale: cost, deployment and accessibility, and hardware requirements:
Cost – whether outsourcing VR training creation or leveraging internal resources, the historic need of expert users to author VR training content has often meant large budgets are required.
Deployment and accessibility – once created, VR training must be deployed throughout an organization and made accessible to end-users. Traditionally, this has meant the creation of a VR-lab/training center or packaging a VR training as an app that must be downloaded.
Hardware requirements – VR training has historically required that end-users use specific VR devices, meaning that adopting VR training throughout an organization often requires a dedicated hardware strategy.
However, with the right technology, proper planning, and stakeholder support, these barriers can easily be overcome:
Reducing costs– a large manufacturing company placed responsibility for VR training creation directly into the hands of their instructors and subject matter experts (SMEs). By leveraging iQ3Connect’s no-code VR authoring tools, they could eliminate the need for dedicated developers and outside vendors and were thus able to streamline the training creation process. Their instructors and SMEs are now able to create VR training as quickly as they could a slide deck.
Frictionless secure deployment and seamless user access – eliminating the need to package VR training as an app that must be downloaded, a Global 500 company in the oil & gas industry used the iQ3Connect platform to make VR training directly accessible on their internal network via a URL link. End users needed only a web browser to access the training. Data security was ensured by leveraging their single sign-on to authenticate users and only allowing internal network access.
No hardware requirements – enterprises from many industries have used iQ3Connect to eliminate VR hardware requirements. Their VR training modules are being made accessible to end users on any AR, VR, PC, or mobile device, eliminating the need for a corporate-wide VR hardware strategy and allowing departments to use the hardware that best matches their circumstances.
The Future of VR Training
Less than a decade ago, VR training regularly cost $500,000 to $1,000,000 for a first deployment. Today, thanks to advancements in the consumer market for VR hardware, standardization of XR technology, and revolutions in XR software, an initial VR training deployment could cost less than $10,000.
This drastic cost reduction, coupled with the availability of VR hardware and support for non-VR hardware, is opening up new use cases and applications for VR training and making it cost effective to deploy VR training throughout an organization.
Moreover, workforces are becoming more globalized, culture is shifting toward hybrid work, and business objectives are being focused on sustainability. These trends, coupled with a drastic skills shortage in the labor force that will increase the demands for training, mean that VR training will be of paramount importance to ensuring industrial companies remain competitive and profitable.
As you start to consider the adoption of VR training, keep in mind some of the traditional barriers to adoption, which might not be obvious in the pilot phase.
Scaling VR training solutions is where many of the challenges arise. However, iQ3Connect is geared to allow organizations to easily overcome the barriers of cost, deployment and access, and hardware requirements, even at scale. Check out some sample VR experiences or talk to one of iQ3Connect’s team members about how VR training can be deployed.