Introduction
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) training, together referred to as Extended Reality (XR), are simulation-based methods that utilize immersive technology to replicate real-world environments and scenarios. They allow users to interact with a computer-generated environment realistically and interactively, typically through an AR or VR headset or tablet. XR training is applicable across various industries such as defense, aerospace, manufacturing, and education to provide hands-on learning experiences without the risks or costs associated with real-world training.
iQ3Connect helps businesses elevate their training programs by providing a platform empowering them to create immersive VR and/or AR experiences tailored to their specific industry needs. But before embarking on an XR training initiative, it is crucial to understand the benefits and limitations of VR and AR training, the impact of XR training on business objectives, and the capabilities of various XR hardware options. The material below provides a guide to navigating and understanding XR training and, more importantly, provides information on how to prepare for and successfully implement an XR training rollout.
Understanding XR Training and Its Benefits
Training with virtual reality or augmented reality provides a myriad of benefits that make it an invaluable tool for industries seeking to enhance their workforce’s skills and capabilities. A detailed assessment of the various benefits is provided in our blog post: Benefits of XR Training, with a short summary provided below:
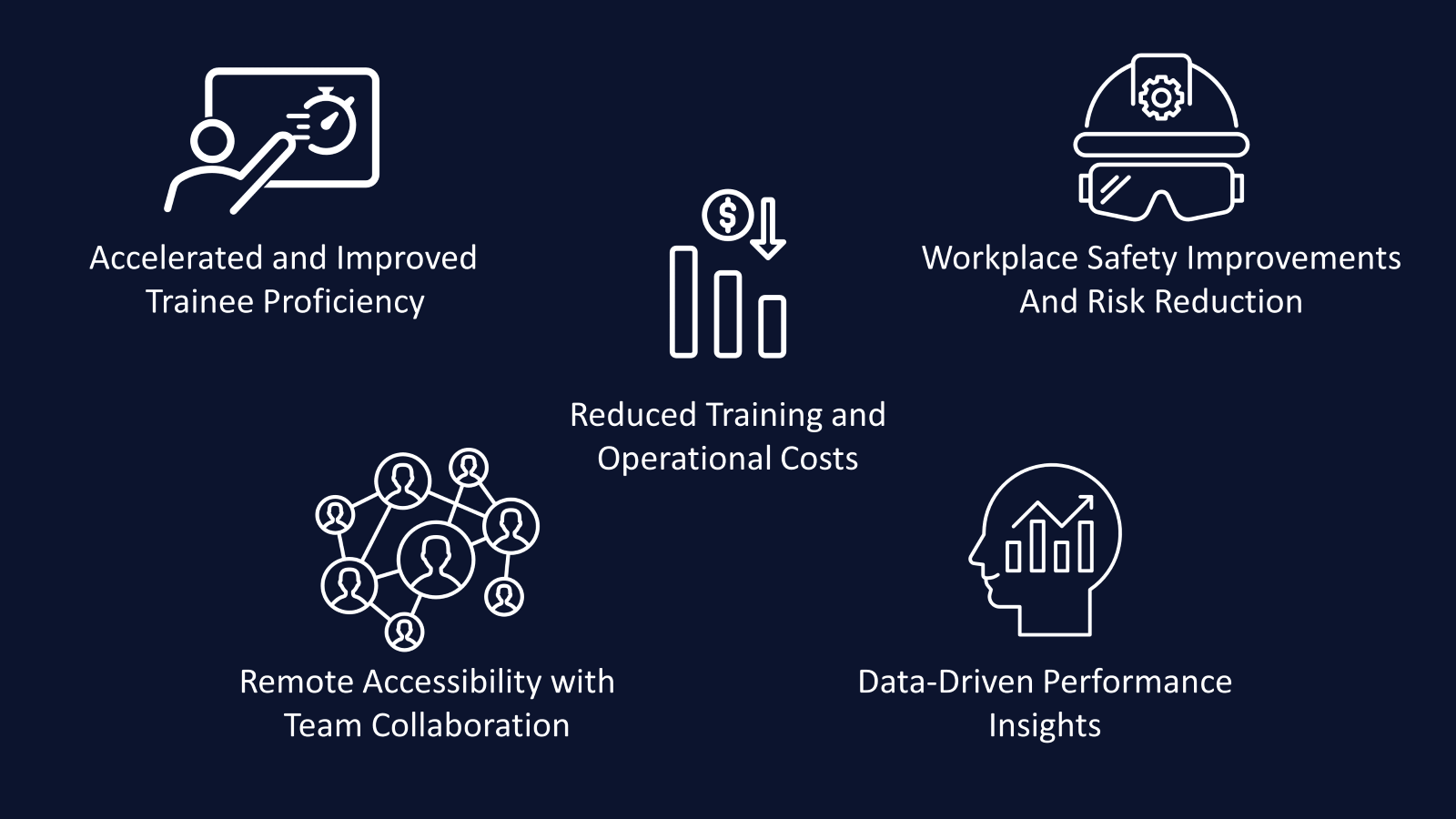
Improved Skill Retention and Accelerated Proficiency
Studies have shown better retention of learned material than traditional methods by using virtual reality and augmented reality for training. The immersive and interactive nature of XR stimulates multiple senses, making information more memorable. Users are more likely to remember what they learn in XR due to the realistic context and experiential learning.
Reduced Training and Operational Costs
While the initial investment in XR technology has historically been a limiting factor in wide-scale adoption, with the latest hardware and software XR training can ultimately be cost-effective almost immediately. It reduces the need for expensive physical training equipment, travel expenses, and facility rentals associated with traditional training methods. Additionally, VR training can be conducted remotely, saving time and resources.
Workspace Safety Improvements and Risk Reduction
VR and AR training improves workplace safety and reduces overall risk in numerous ways. First, by virtualizing certain training scenarios, a safe environment is created where a trainee can practice and learn without the safety risks that would accompany real-world errors and mistakes. Secondly, XR training provides opportunities for trainees to react and address hazards that are too risky, costly, or infeasible to recreate physically.
Remote Collaboration and Expert Guidance
AR and VR training enables geographically dispersed teams to train together in a virtual environment, fostering teamwork and knowledge sharing. Additionally, subject matter experts can remotely monitor trainee progress, provide on-the-job coaching, and intervene during simulations to ensure compliance with best practices and safety standards. XR training also saves time by providing convenient access from anywhere, eliminating travel needs.
Data-Driven Performance Insights
VR and AR training offer unrivaled in-depth data capture on trainee performance which businesses can use to optimize training methods and improve training outcomes. This data can not only be used to help improve individual trainee outcomes but can also be aggregated to provide important insights into the overall performance of the training program, enabling identification of areas for improvement.
Implementing XR Training to Achieve Business Objectives
Understanding the benefits of AR/VR training is not enough to ensure that an XR training initiative is funded or successfully completed. A systematic approach is required to ensure that the training initiatives contribute directly to the organization’s overall goals. Based on our most successful customer engagements, we have distilled this systematic approach into six primary steps:
Identify Business Objectives
Start by clearly defining the goals and objectives of the learning initiative and the organization as a whole. The learning objective should have a SMART approach: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also align with your company goals, such as increasing employee productivity, reducing operational costs, enhancing customer satisfaction, or reducing errors.
Conduct a Training Needs Assessment
Evaluate the specific skills, knowledge, or competencies that employees need to achieve the identified business objectives. Determine any gaps in existing training programs that XR technology could address effectively.
Define XR Training Objectives
Based on the training needs assessment, establish clear and measurable objectives for XR training initiatives. These objectives should align closely with the identified business goals and specify the desired outcomes of the training program.
Create XR Training Content
Create XR training content that is tailored to address the specific skills and competencies required to meet the organization’s objectives. Ensure that the content is relevant, engaging, and aligned with the learning preferences of the target audience.
Integrate XR Training into Existing Workflows
Integrate XR training seamlessly into employee’s workflows to ensure that they can apply newly acquired skills directly to their job responsibilities. This could involve incorporating XR simulations into onboarding programs, ongoing skills development initiatives, or performance improvement plans.
Measure ROI and Adjust as Needed
Evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of XR training initiatives by comparing the achieved outcomes against the initial business objectives and associated costs. Use this data to make informed decisions about the future of XR training programs and adjust strategies as needed to optimize effectiveness.
Choosing the Proper XR Training Software and Hardware
XR Hardware
The first decision to be made when choosing XR hardware is whether to focus on augmented reality or virtual reality. Most devices on the market are exclusively AR (such as the HoloLens and MagicLeap) or VR (such as the HTC Vive), but the latest devices (such as the Meta Quest 3 or Apple Vision Pro) offer both AR and VR modes. The next decision often involves choosing between standalone or tethered devices. Standalone XR headsets offer wireless, self-contained systems for maximum portability but can have limited capability to display complex 3D models. Tethered XR headsets which connect to a PC to leverage powerful graphics cards, provide higher-quality graphics and performance but are limited in their portability. Consider mobility, budget, graphical needs, and enterprise support when selecting AR or VR hardware so that it aligns with training objectives and user experience requirements.
Another important factor to consider is that the XR hardware choice may not be entirely in your control. Different groups and teams may already have XR hardware. As the hardware space continues to adapt and improve, new hardware may be acquired by the business.
XR Software
Choosing the right software platform is crucial for the future success of any AR and/or VR training initiative. The software platform must offer a range of tools for creating immersive and interactive 3D environments and be compatible with the chosen (and or available) XR hardware. It must also be flexible enough to accommodate updates and modifications to the training content and be suited to the skill set of the training content creators. The most important factors to consider are:
Compatibility
Ensure that the XR software is compatible with your existing systems and infrastructure. Verify compatibility with operating systems, XR hardware, and other software applications used within your organization. Can the XR experience easily be deployed, managed, and monitored by your existing business tools?
Scalability
Choose an XR platform that can scale to meet your organization’s growing training needs. Can the XR platform easily support 100’s or 1000’s of users? Can the trainers and content creators build and deploy XR training without extensive development or modeling skills? Can the XR platform leverage the existing IT and Administrative toolsets to eliminate duplicate efforts for user access and authorization?
Training Creation and User Experience
To ensure technical accuracy and cost-effectiveness, choose an XR platform that empowers the trainers, subject matter experts, and/or content creators themselves to create XR experiences. While high-quality visuals are appealing, the cost and time of creating them must be considered and balanced against their benefit for a given use case.
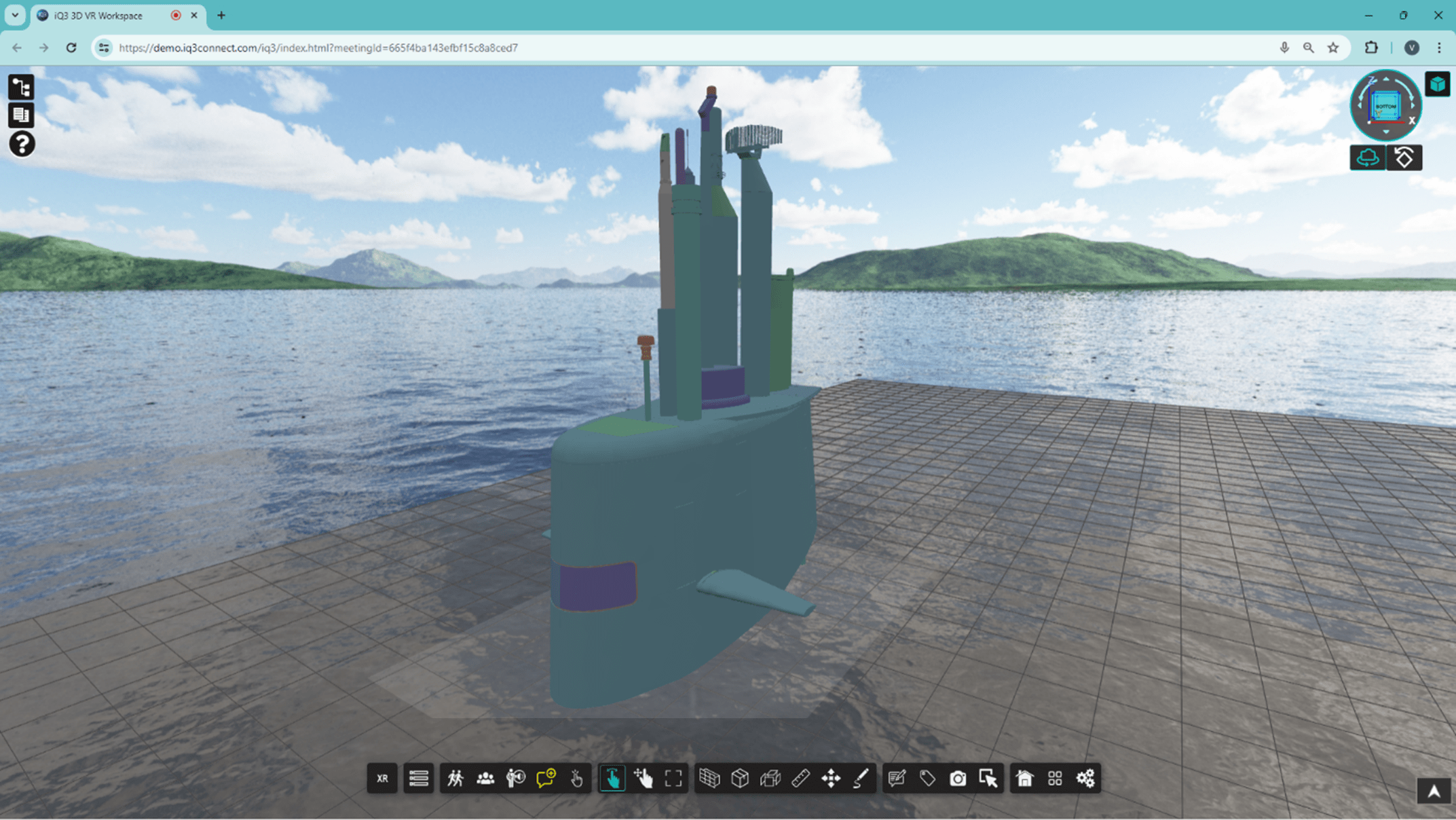
iQ3Connect’s web-based training platform enables enterprises to scale XR training across the enterprise. With just a web browser, individuals can engage in immersive training sessions using any AR or VR headset, or opt for 2D interactive experiences on PCs, tablets, or mobile devices. Seamlessly deploy single-user, self-paced training modules and/or host instructor-led training in multi-user virtual classrooms to foster collaboration. Moreover, our platform integrates seamlessly into LMS to monitor trainee performance and knowledge retention. Lastly, by providing a user-friendly solution, the iQ3Connect platform empowers trainers and subject matter experts to build and/or customize XR training without the need for modeling or development expertise.
Developing an XR Training Rollout Plan
Creating an effective VR or AR training initiative not only depends on a systematic approach to matching learning objectives with business goals but also on a robust rollout plan to stakeholders and end users. In our engagements with key customers, successful rollouts have generally involved the following:
- Assessment: Identify training objectives and assess the specific skills or knowledge gaps that XR training will address.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve key stakeholders, including trainers, managers, and end-users, to gather input and buy-in for the rollout plan.
- Training Creation: Create (or outsource the creation of) XR training content based on the identified training objectives. Involve key stakeholders in the creation process.
- Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot tests with a small group of users to evaluate the effectiveness of the XR training program and gather feedback for improvements.
- Production Preparation: Make adjustments and changes based on feedback from pilot testing. Integrate the XR content into existing business tools (such as Learning Management Systems) to reduce IT and administrative burdens as usage increases.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for collecting feedback from users throughout the rollout process to identify improvement areas and promptly address any issues.
- Scalability Planning: Ensure that the XR training program is scalable to accommodate a growing number of users, additional training content, and expanding training requirements over time.
- Continuous Improvement: Use feedback and performance data to iteratively improve the XR training program, update content, and refine rollout strategies as needed.
Training Your Team for XR Training
Training with the use of XR technology can benefit employees of all ages and backgrounds, but as XR is still a new modality, it is important to ensure users are adequately acclimated to XR technology, without distracting from the core training content. And as with other training modes, it’s important to address multiple styles of learning. A few key things to consider, include: .
Upgrade Materials
Update training resources to cover XR technology and its use. Consider creating a dedicated XR user manual and an interactive presentation for enhanced learning.
Demonstrate XR
Provide hands-on demonstrations of VR and AR technology to supplement traditional training methods and engage employees.
Engage XR Interactivity in Stages
Use immersive videos, virtual walkthroughs, and virtual equipment demonstrations with varying and increasing levels of interaction to acclimate employees gradually to all the capabilities of a XR training.
Hands-On Challenges
Introduce XR gradually with interactive challenges to build confidence and familiarity. Conduct interactive quizzes post-training.
Navigating the XR Training Maze: Solutions to Common Hurdles
Technical Complexities
Setting up and maintaining XR systems may pose technical and IT challenges. IT departments may authorize only a small subset of possible XR headsets to be used within the organization, while software management and application installation may prove impractical.
However, with iQ3Connect, our web-based approach not only allows any XR (and non-XR) device to be used but also means that only a web browser is required to access training content, eliminating the need for software downloads and application management. This enables teams to focus on the content (and not the technology) and seamlessly deploy immersive experiences that are accessible from anywhere, secured by your existing IT infrastructure, and tracked by LMS.
Cost Barriers
XR hardware and software have historically been expensive, but with the latest consumer-grade hardware costs can be drastically reduced. Even with legacy solutions, XR adoption is shown to have a positive return on investment (ROI). Studies have shown that AR/VR-based training reduces enterprise training time by up to 40% and also helps save 30-70% in training costs compared to traditional methods.
With easy-to-use XR software platforms like iQ3Connect, XR costs are further reduced. With iQ3Connect, an initial Proof-of-Concept can cost less than $10,000 USD, whether created by an internal team or a 3rd party. Moreover, the iQ3Connect platform empowers trainers and subject matter experts to build XR experiences independently, reducing long-term costs.
User Skill-Shortages
Subject matter experts and training content creators often lack extensive developer or 3D modeling experience, presenting a significant barrier to effectively implementing traditional XR software for training purposes. This knowledge gap can hinder the creation of immersive training content and limit the potential benefits of XR technology within organizations.
iQ3Connect addresses this challenge by providing no-code tools, visual creation features, and powerful automation tools. These user-friendly capabilities empower anyone, regardless of technical background, to build immersive training content with ease. By removing the need for coding expertise and simplifying the content creation process, iQ3Connect enables subject matter experts and content creators to leverage their domain knowledge effectively. This fosters the creation of engaging and impactful training experiences, unlocking the full potential of XR technology within organizations while overcoming the limitations posed by traditional XR software.
Conclusion and Call to Action
AR and VR training offers improved skill retention and accelerated proficiency compared to traditional methods across various industries. Moreover, it substantially reduces training and operational costs by eliminating the need for expensive physical equipment and travel expenses through remote training capabilities. Additionally, XR training enhances workplace safety by simulating hazardous scenarios in a risk-free environment, fosters remote collaboration and expert guidance, and offers invaluable data-driven performance insights for optimizing training outcomes. Implementing VR and AR training to meet business objectives involves identifying specific goals, conducting needs assessments, creating tailored content, and seamlessly integrating it into existing workflows. By selecting appropriate VR and/or AR hardware and software and developing robust rollout plans, the chances for successful execution of XR training initiatives greatly increase.
iQ3Connect’s AR/VR web-based platform empowers enterprises to achieve successful XR training adoption by eliminating technical and cost barriers and enabling anyone to build XR training content. Moreover, our device-agnostic approach future-proofs your XR investment by ensuring you can continue to use XR content regardless of hardware changes.
Experience the benefits firsthand at www.iq3connect.com or sign up for a free trial at https://iq3connect.com/try-free. Transform the way your workforce learns and develops, anytime, anywhere!