As we discussed in a previous blog post, Leveraging VR/AR Technologies to Address Skill Shortages and High Workforce Turnover, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) training offers substantial cost-savings opportunities for manufacturing and industrial enterprises and is a vital tool for addressing the skills gap and high workforce turnover rates affecting these enterprises. In this blog, we delve deeper into the specific applications, benefits, and unique features that make VR and AR indispensable tools for industrial training.
History of VR and AR in Industry Training
The application of VR and AR in industrial training has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, these technologies were primarily used in specialized fields like aerospace and defense. However, as hardware became more affordable and software more sophisticated, VR and AR have found applications across a range of industries, from manufacturing to energy to construction.
- Early Adoption: Aerospace and defense were among the first to adopt VR and AR for training, given the high-risk nature of these fields.
- Mainstream Acceptance: As the technology matured, sectors like manufacturing, energy, and construction started integrating VR and AR into their training modules.
- Current Trends: Today, with the advent of more affordable and user-friendly devices, VR and AR are becoming standard tools for industrial training across various sectors.
Future of VR and AR in Industrial Training
As technology continues to advance, the future of VR and AR in industrial training looks promising. With the advent of 5G, cloud computing, and AI, we can expect even more immersive and interactive training experiences. iQ3Connect is committed to staying at the forefront of these advancements to offer the most effective and engaging training solutions.
Benefits of VR and AR in Industrial Training
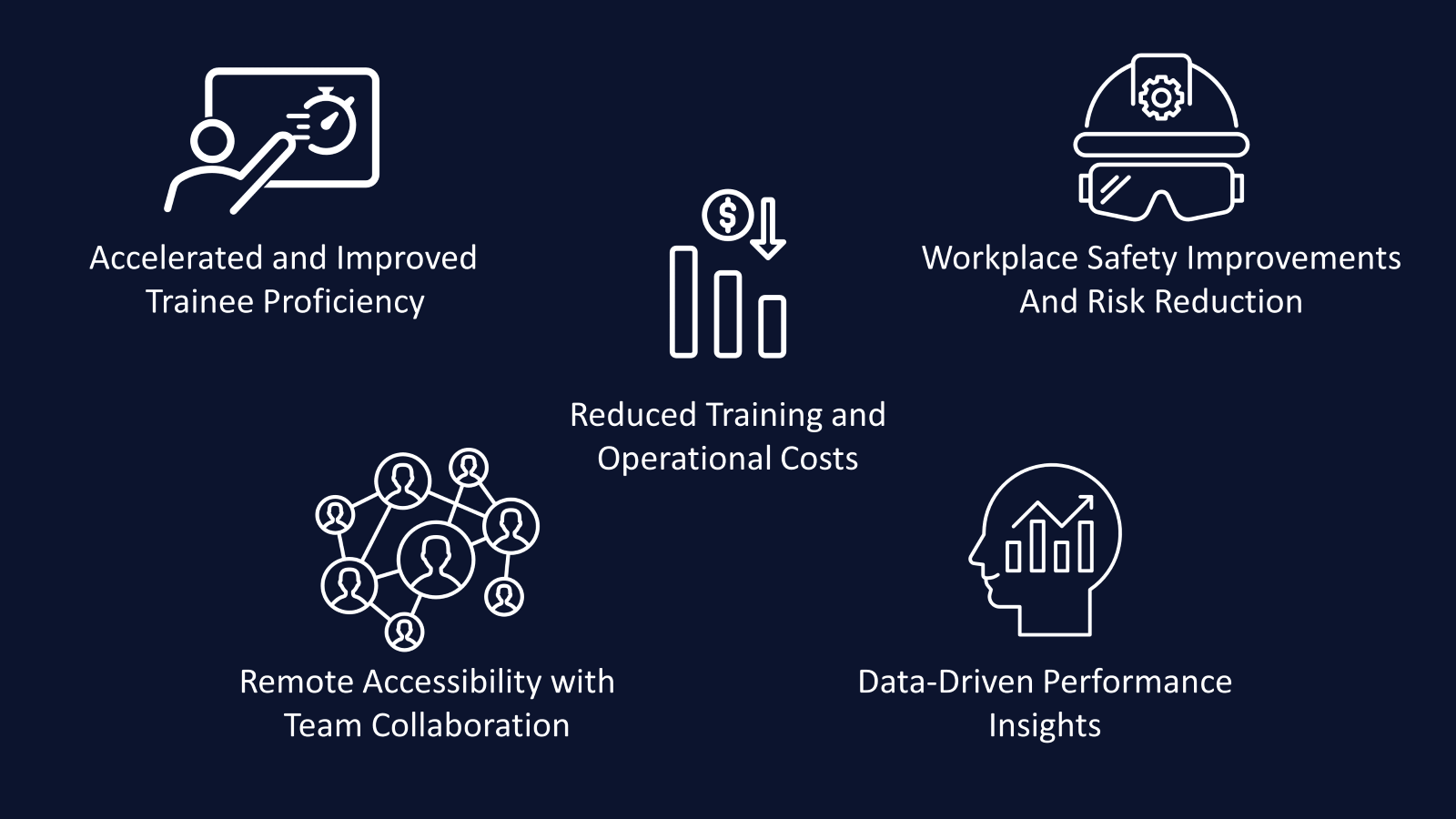
Both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) offer a plethora of benefits that make them indispensable tools in industrial training. Here are some key advantages:
- Safety: Both VR and AR allow for risk-free training in simulated environments, reducing the likelihood of accidents during training.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Virtual training eliminates the need for physical materials and logistics, thereby reducing costs.
- Efficiency: VR and AR training modules can be easily updated or modified, saving time and resources in the long run.
- Engagement: The interactive nature of VR and AR increases learner engagement, which in turn improves retention rates.
- Real-Time Feedback: Both technologies offer real-time analytics and feedback, enabling continuous improvement in training programs.
Virtual Reality (VR) in Industrial Training
In virtual reality (VR), users are fully immersed in a 3D environment, disconnected from the physical world. This complete immersion allows for the display of entire facilities or equipment that wouldn’t fit in a physical space. VR headsets like Oculus Quest 2, Windows Mixed Reality HP Reverb G2, and the HTC Vive family of products are commonly used for this purpose.
Applications for VR in Industrial Training
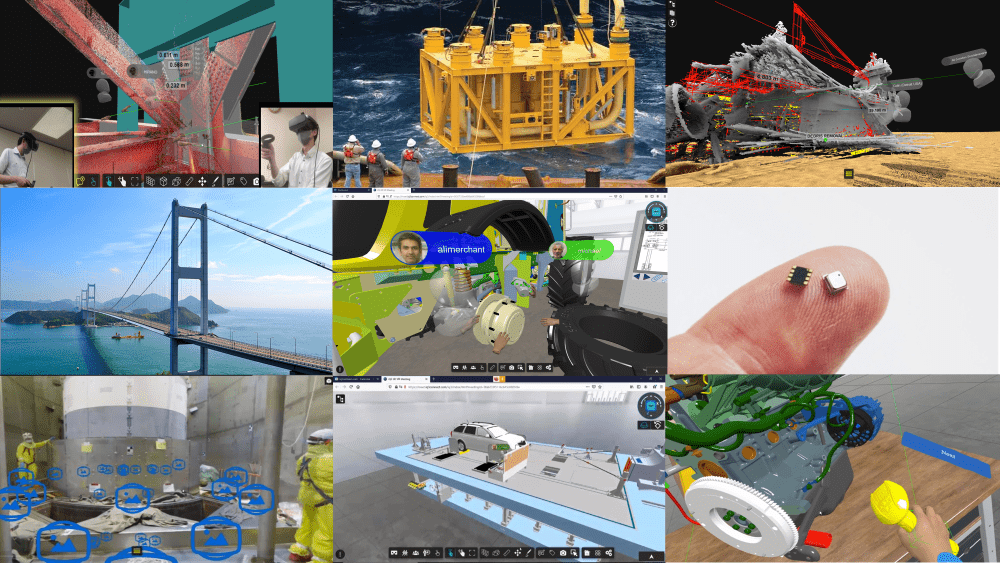
- Health, Safety, and Environment Training: Trainees can walk through a digital twin of the facility to identify potential hazards, exit pathways, and safety procedures. Virtually create hazardous situations to test identification and response procedures.
- Maintenance and Operations Training: Technicians can practice maintenance operations on equipment that is difficult or impractical to physically train with, such as undersea structures. Avoid plant shutdowns by training on a digital mock-up of the equipment instead of the physical equipment.
- Assembly and Virtual Build: Prepare your workforce for a new product line or train your customers and partners on product assembly before it arrives by practicing assembly operations virtually.
- General Knowledge: Improve trainee retention by replacing slide decks and videos with interactive and immersive virtual training.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Industrial Training
In augmented reality (AR), users can see both the real world and the virtual world simultaneously. Devices like the HoloLens and various mobile devices are commonly used for AR applications.
Applications for AR in Industrial Training
- Health, Safety, and Environment Training: Display virtual information, hazards, exit paths, etc., as a user walks through the physical structure.
- Field Maintenance and Operations: Display virtual work instructions and operating procedures overlaid on the physical equipment as technicians perform their tasks. Leverage expertise from remote experts for real-time collaboration.
- Assembly and Virtual Build: Trainees can view virtual work instructions overlaid on the physical object as they assemble the actual structure.
- Product Knowledge: Improve trainee comprehension of complex products by providing mixed virtual and real-world training environments, combining real-world interaction with virtual overlays of text and graphics.
Technical Specifications for Implementing VR and AR in Industrial Training
When considering the adoption of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) into your industrial training programs, understanding the technical requirements is crucial for effective implementation. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Hardware Requirements
- VR and AR Devices: Various headsets and devices are available on the market. It’s essential to choose hardware that aligns with your training objectives and is compatible with your chosen software solution. As a device agnostic platform, iQ3Connect is compatible with nearly all VR, AR, PC, and mobile devices.
- Computing Power: While many solutions require high-performance computers with robust graphics cards, iQ3Connect’s proprietary rendering technology eliminates this need, making the setup more accessible.
- Network Infrastructure: Many VR and AR solutions require dedicated IT support for managing applications and end-user devices. With solutions like iQ3Connect, which operate through an internet browser, no such management is required.
2. Software Requirements
- Platform Compatibility: Ensure that the VR or AR software you choose can integrate seamlessly with your existing training management systems.
- User Interface: Look for software with an intuitive user interface to minimize the learning curve for both trainees and administrators.
- Content Creation Tools: Some platforms offer built-in tools for creating custom training modules, which can be a significant advantage. Integrated 3D model import and automatic model optimization are critical to ensuring that anyone can create industrial training.
3. Maintenance and Updates
- Software Updates: With browser-based solutions like iQ3Connect, updates are seamless, requiring no manual intervention, thus keeping the training modules current and secure.
4. Security Considerations
- Data Encryption: Make sure the platform you choose complies with data protection regulations and uses encryption to secure sensitive information.
- User Authentication: Features like single sign-on and integrations into access control lists can add an extra layer of security and leverage existing corporate security measures.
- Data Storage: Application downloads can leave sensitive data stored on local devices and thus vulnerable to unauthorized access or theft.
5. Enterprise/Business Integration
- Cloud vs. On-premise Deployment: Any practical VR and AR solution must support on-premise (or private data center) installation. However, as enterprises adopt and expand cloud services these solutions must also be cloud compatible.
- Integrations: Support for business tool integrations (such as email, PLM, LMS, Active Directory, etc.) is vital to fully support broad and everyday access for global workforces.
Understanding these technical specifications will enable decision-makers to make more informed choices when selecting and implementing VR and AR solutions for industrial training. iQ3Connect’s browser-based platform simplifies many of these considerations, making it an accessible choice for organizations of all sizes.
Final Considerations
Many of the same use cases are suitable for either VR or AR training, and the choice will often depend on the specifics of the use case. However, VR generally offers some consistent benefits over AR, such as ease of training creation and modification, quality of visuals, and cost-effectiveness of headsets. The iQ3Connect Platform makes the VR vs. AR debate less critical when choosing a training solution, as any training or experience created can be used on any device, whether VR, AR, PC, or mobile.
The choice between VR and AR often comes down to the specific needs of the industry and the availability of physical space and equipment. With iQ3Connect, you have the flexibility to choose the best solution for your training needs. Ready to revolutionize your industrial training programs? Contact us today to learn more.